
The rain test method is a vital procedure used across various industries to evaluate the resistance and durability of materials, products, and structures against water exposure. This testing method simulates real-life rain conditions to assess how well items can withstand precipitation without compromising their functionality or integrity. From electronics to automotive parts, construction materials, and outdoor equipment, the rain test ensures that products meet stringent quality and safety standards before reaching the consumer.
Purpose of the Rain Test Method
The primary purpose of the rain test method is to determine a product’s ability to resist water penetration and function correctly under rainy conditions. This is crucial for several reasons:
- Weather Resistance: Products intended for outdoor use must endure varying weather conditions, including heavy rainfall. The rain test verifies their resilience against such elements.
- Safety: For certain products, especially in the automotive and aerospace industries, water ingress can pose serious safety risks. Testing helps identify potential hazards and design flaws.
- Longevity and Durability: Continuous exposure to rain can deteriorate materials over time. Rain tests help in evaluating the long-term effects of water exposure, ensuring products remain durable throughout their expected lifespan.
- Compliance and Standards: Many industries have strict regulations and standards regarding water resistance. The rain test helps manufacturers ensure compliance with these requirements.
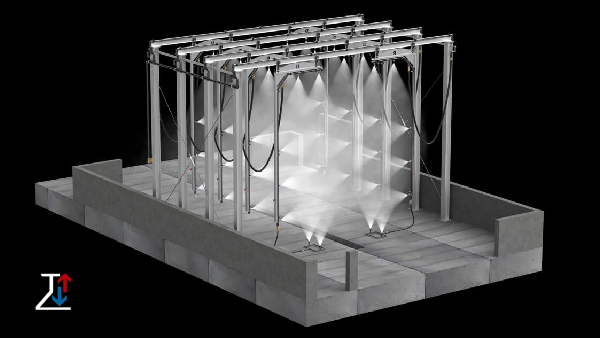
Types of Rain Tests
There are several types of rain tests, each designed to simulate different aspects of rainfall and water exposure. Common types include:
- Drip Test: This involves dripping water onto the product from a specified height to evaluate its resistance to light, continuous water exposure. It is commonly used for electronics and small appliances.
- Spray Test: This test involves spraying water at various angles and pressures to simulate rain conditions more accurately. It helps determine how well a product can handle direct water impact.
- Immersion Test: Although not strictly a rain test, immersion tests involve submerging the product in water to assess its resistance to water penetration. This is especially relevant for products that might be exposed to standing water.
- Jet Test: This involves subjecting the product to high-pressure water jets to simulate heavy rain or water impact, testing the product’s structural integrity and water resistance.

Rain Test Procedures
The rain test method follows a standardized procedure to ensure consistency and reliability of results. The general steps include:
- Preparation: The product is prepared according to the test requirements. This may include installing it in a specific orientation or applying power if it is an electronic device.
- Testing Environment: The test is conducted in a controlled environment, such as a rain chamber, where temperature, humidity, and water pressure can be regulated.
- Water Application: Water is applied using the selected method (drip, spray, jet, etc.). The duration, angle, and intensity of water application are controlled to simulate real-life conditions.
- Observation and Measurement: During and after the test, the product is closely observed for signs of water ingress, structural damage, or functional impairment. Instruments may be used to measure water penetration and other parameters.
- Documentation: Detailed records are kept of the test conditions, observations, and results. This documentation is crucial for quality control, certification, and further analysis.
Industry Applications
The rain test method is employed across a wide range of industries, each with specific requirements and standards:
- Automotive Industry: Vehicles and their components, such as headlights, windshields, and seals, undergo rain tests to ensure they can withstand driving in heavy rain without leaking or malfunctioning.
- Electronics and Appliances: Devices like smartphones, outdoor lighting, and household appliances are tested for water resistance to prevent electrical failures and ensure user safety.
- Construction and Building Materials: Roofing materials, windows, and exterior finishes are subjected to rain tests to verify their ability to keep buildings dry and structurally sound.
- Aerospace: Aircraft components and materials are tested to withstand rain and other adverse weather conditions during flight and on the ground.
- Outdoor Equipment: Products like tents, backpacks, and protective gear are tested to ensure they remain functional and durable when exposed to rain.
Advantages of the Rain Test Method
The rain test method offers several benefits:
- Enhanced Product Quality: By identifying and addressing potential issues related to water exposure, manufacturers can improve the quality and reliability of their products.
- Risk Mitigation: Early detection of water resistance problems helps prevent costly recalls, repairs, and potential safety hazards.
- Customer Satisfaction: Products that perform well in rain tests are more likely to meet customer expectations, leading to higher satisfaction and brand loyalty.
- Regulatory Compliance: Conducting rain tests helps manufacturers comply with industry standards and regulations, facilitating market access and certification.
Conclusion
The rain test method is an essential procedure in product development and quality assurance across various industries. By simulating real-world rain conditions, it ensures that products are safe, durable, and reliable even in adverse weather conditions. As technology advances and consumer expectations rise, the importance of rigorous testing methods like the rain test continues to grow, helping manufacturers deliver high-quality products that stand the test of time.